
MOTHER'S CONDITIONS
CONDITIONS OF THE MOTHER THAT MAY AFFECT THE BABY
Page Content:
- Diabetes
- Size matters
- High blood pressure
- Infection - Group B strep infection
- Cervical cerclage
- Preterm or premature labor
- Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes (PPROM)
- Chorioamnionitis
- Induction of labor
Diabetes: All pregnant women are screened for diabetes during their pregnancy. If your testing indicates you have diabetes with your pregnancy or if you had diabetes before you were pregnant, your healthcare provider will order additional testing to be done to ensure the baby is not growing too large. Additional testing may include ultrasound examinations and non-stress testing. If your healthcare provider determines the baby is too large to fit through the birth canal due to diabetes, a cesarean section delivery may be advised.
Size matters: If a baby is too large or the pelvis is too small, the baby may get stuck and become injured during the attempted vaginal delivery. Shoulder dystocia can occur, which may result in partial or permanent nerve injury to the affected shoulder, arm, and hand of the baby.
High blood pressure (Preeclampsia, Gestational Hypertension, Pregnancy Induced Hypertension): A slow or sudden onset of high blood pressure after 20 weeks gestation can lead to complications for the mom and baby. If left uncontrolled, this can be fatal for the mom and baby. Signs and symptoms of high blood pressure during pregnancy may include: excess protein in the urine, severe headaches, visual changes, epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, decreased platelet level, shortness of breath, sudden weight gain and swelling, and impaired liver and kidney functioning. High blood pressure may be managed with modified activity, medications, and close monitoring of the mom and baby. Delivery of the baby is the most effective treatment but if it’s too early in the pregnancy for delivery, then medications, modified activity, and close monitoring are the treatment of choice.
Infection - Group B strep infection: Group B streptococcus infection is also known as GBS or Group B strep. This infection can cause severe illness and may cause death in newborns. Because of this, pregnant mothers are tested for the presence of GBS during their pregnancy, usually close to 36 weeks gestation. If the test is positive, the mother is treated during labor with IV antibiotics to prevent the spread of GBS to the baby. If untreated or treated insufficiently, newborns can develop pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis and may die.
Cervical cerclage: When a woman is not pregnant, her cervix, which is the bottom part of the uterus that opens up and thins out, is normally long, closed, and firm. Some women have a short cervix that may begin to open too early during pregnancy, leading to miscarriage or premature delivery. In an attempt to prevent this, a cervical cerclage using tape or sutures is sometimes placed.
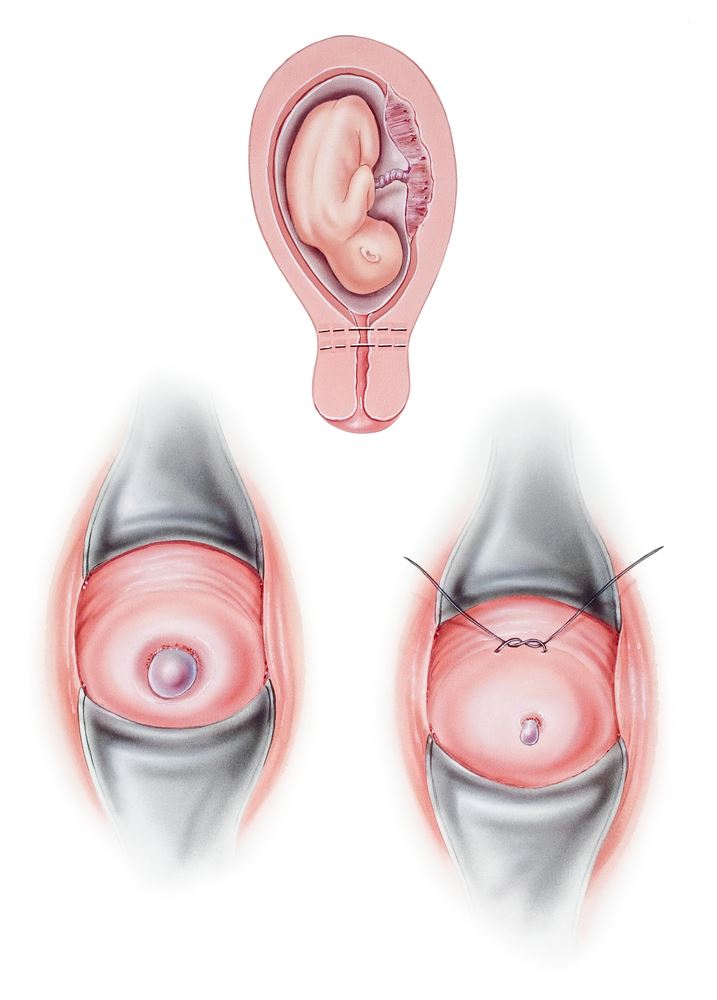
Preterm or premature labor: Preterm labor is defined as regular contractions that dilate the cervix after 20 weeks and before 37 weeks of gestation. Preterm labor can end in the delivery of a premature baby that may need care in a neonatal intensive care unit. The more premature a baby is born, the more care the baby is likely to require. Risk factors for preterm labor include delivering prematurely in a previous pregnancy, multiple babies such as twins or triplets, infection, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, too much amniotic fluid also known as polyhydramnios, and bleeding.
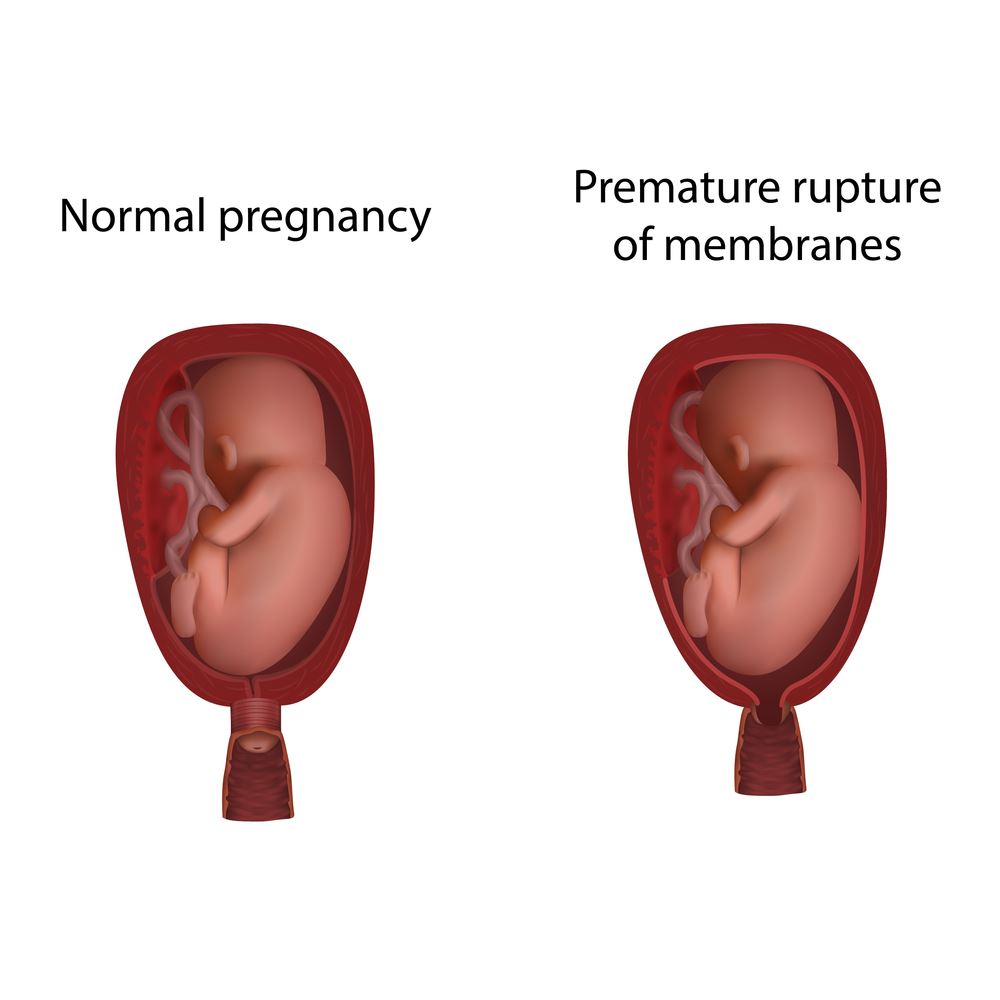
Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes (PPROM): Preterm premature rupture of membranes occurs when your water breaks before 37 weeks gestation. Complications of PPROM include infection in the mom and/or baby and premature birth. If PPROM occurs without the mom in labor, the treatment may include steroids to aid in maturing the lungs of the baby, antibiotics to prevent infections, and monitoring of mom and the baby to ensure the well-being of mom and baby.
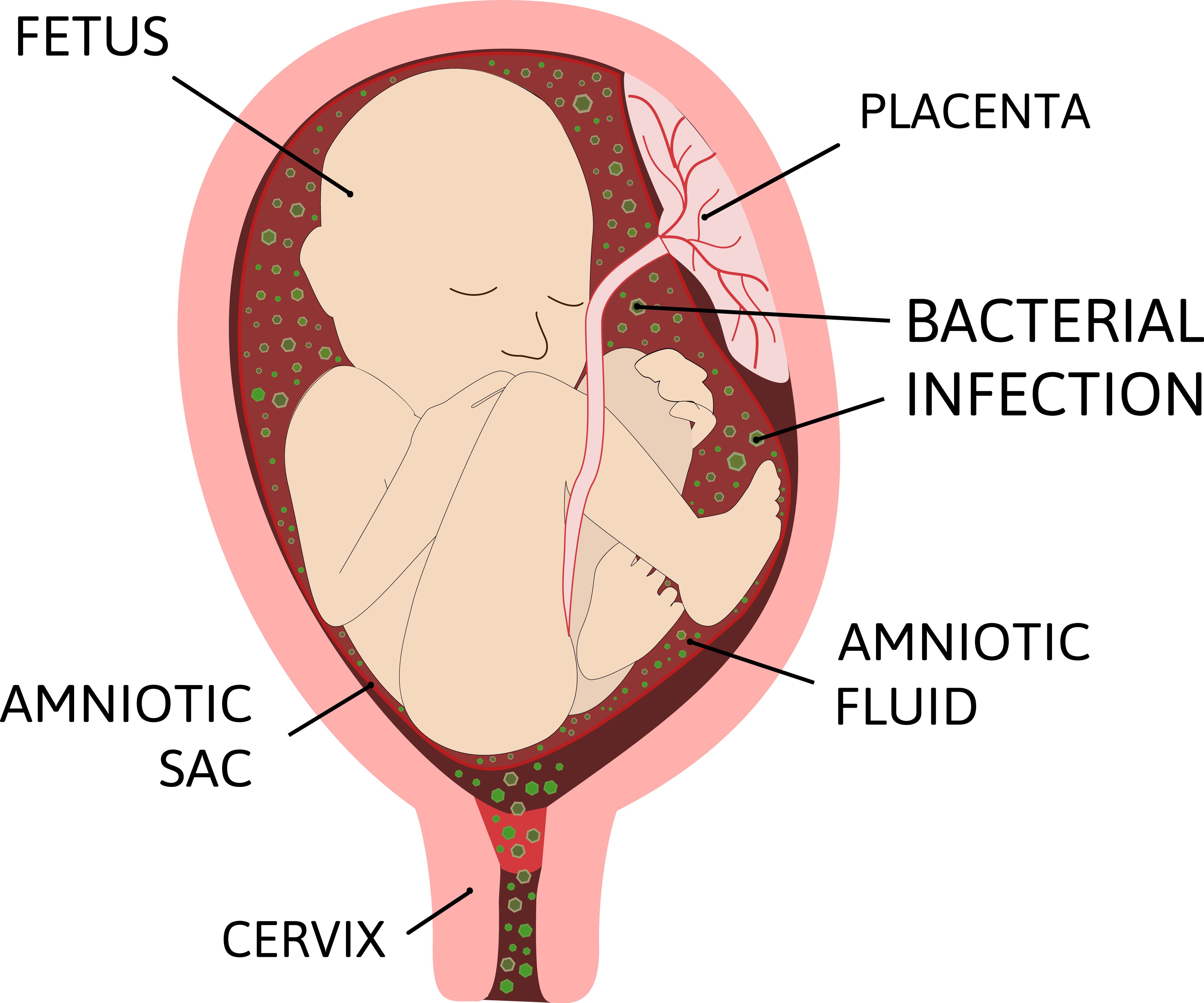
Chorioamnionitis: Chorioamnionitis is an infection of the uterus, amniotic sac and/or fluid during pregnancy. This can cause preterm labor and premature delivery of the baby. Treatment includes antibiotics, close monitoring of the mom and baby, and may include induction of labor and/or expedited delivery.
-
"Supportive and clear communication."
- Cathleen O. -
"A positive experience from the start. He found things other lawyers did not find. Those things were not all easy to find out. He delivered hard to hear facts about the case in as good a way as you could hope."
- Ryan -
"Mr. Bereston represented me in my case. I found him to be very knowledgeable, professional and easy to talk to about any questions I had concerning my case. He would always promptly return my calls if I had any concerns or questions as the case went on."
- Clyde G. -
"They truly love what they do and love each and every one of their clients like they are their own family."
- Shauna G.
- Induction of labor: There are several methods and medications that your healthcare provider may use to induce (start) your labor.
- Insertion and inflation of a balloon catheter is one method that may be used. This involves the placement of a tube that has two small balloons on the end. This is inserted so that a balloon is on each side of the cervix. The balloons are then inflated with water.
- Artificial rupture of membranes (AROM) or breaking the bag of waters is sometimes used to stimulate labor. The decrease in the fluid can cause the umbilical cord to become compressed, causing nutrient and oxygen exchange to be interrupted or blocked.
- Cytotec (misoprostol) is a medication that may be placed in your vagina or may be given orally to stimulate contractions. It may be placed or given orally once or several times depending on the presence of contractions. Too many contractions, contractions that are too strong, or contractions too close together are dangerous side effects that may occur when this medication is used. The baby obtains and exchanges oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients with the placenta via the umbilical cord mainly when the uterus is resting between contractions. If too many contractions that are too strong and too long occur, this exchange cannot be fully made which deprives the baby of oxygen and nutrients cannot be adequately exchanged.


Our goal in each case we handle is to obtain the maximum compensation for our clients, which is why we only take on a limited number of cases each year.